Why And When To Use Radiocarbon Dating
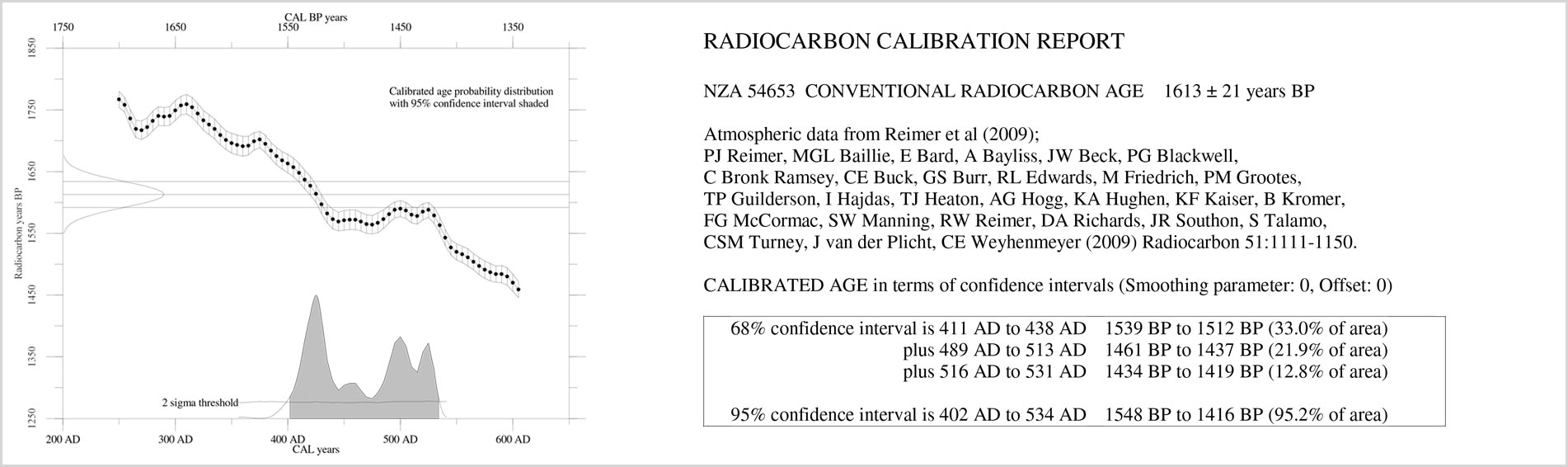 Snippet from a radiocarbon calibration report.
Snippet from a radiocarbon calibration report.
Radiocarbon Dating
Optical microscopy study of exterior surfaces can find evidence of alteration, such as over-painting and modern tool marks, as well as evidence of antiquity, such as fossilized organic matter. It is often one of the first examinations performed on an object, and is commonly used to determine the necessity and order of further examination. The non-invasive technique is frequently performed in conjunction with a microscopic examination of the internal structure of a removed sample.
Advantages
- Using Accelerator Mass Spectrometry radiocarbon as compared to “conventional” testing, the sample size is very small.
- It can be performed on a broad range of organic materials.
- The margin of error is relatively small.
- There is a large database for comparison.
- It is available from a large number of facilities.
- It can be used to date certain types of iron objects.
Disadvantages
- Even with prepaid expedited service, the test requires at least four weeks to obtain results, generally longer.
- It is moderately expensive, up to $1000 including shipping and sampling.
- The sample is destroyed, so no further tests can be performed on it.
- Certain contaminates can cause a wider margin of error or even a complete misread, even though all reliable facilities do various decontamination procedures prior to testing.